G-Force Chart
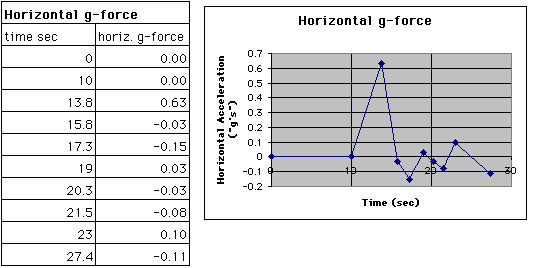
| Reading Pt | Elapsed Time | Time
sec |
Initial Velocity
m/sec |
Final Velocity
m/sec |
Acceleration
m/sec2 |
Horizontal
g's |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0-1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 7.1 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1-2 | 13.8 | 3.8 | 7.1 | 30.6 | 6.18 | 0.63 |
| 2-3 | 15.8 | 12.0 | 30.6 | 27.6 | -0.25 | -0.03 |
| 3-4 | 17.3 | 5.3 | 27.6 | 20.0 | -1.43 | -0.15 |
| 4-5 | 19.0 | 13.7 | 20.0 | 24.0 | 0.29 | 0.03 |
| 5-6 | 20.3 | 6.6 | 24.0 | 22.0 | -0.30 | -0.03 |
| 6-7 | 21.5 | 14.9 | 22.0 | 10.0 | -0.81 | -0.08 |
| 7-8 | 23.0 | 8.1 | 10.0 | 18.0 | 0.99 | 0.10 |
| 8-9 | 24.7 | 16.6 | 18.0 | 0 | -1.08 | -0.11 |
Horizontal Acceleration measured in g's (m/sec2)
Horizontal Acceleration (measured in g's) is the acceleration that produces the force that pushes you back into the seat (as oopposed to vertical g-force which is the force that pushes you down into the seat). In real life, there are vertical, horizontal, and lateral g-forces.Velocity is the change in position over time. Acceleration is the change in velocity over time. G's can be used to express acceleration. On earth, 1g= produces an acceleration of 9.8 m/sec2 on an object in free fall. To calculate acceleration, find change in velocity, then divide by time. To calculate the horizontal g's, divide acceleration by 9.8 m/sec2.